README
Install APIC V10 on Amazon EKS
- Install APIC V10 on Amazon EKS
- Summary
- Create EKS Cluster
- Download APIC Related CRDs
- Install Ingress and Cert Manager
- Configure Route53 DNS
- Apply CRDs and Customize APIC Subsystem Deployment
- Update Node vm.max_map_count
- Cluster Access/Management
- References
Summary
This guide is a quick and consolidated reference on how to install APIC on EKS. This will create a cluster for the purposes of DEV and POC. The cluster sizing, profiles and licenses selected in the sample files are not meant to be used for a production cluster.
Always refere to the Knowledge Center for installation details: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSMNED_v10/com.ibm.apic.install.doc/tapic_install_Kubernetes.html
Assumptions:
- Non-Prod license and sizing
- Online install using IBM entitled registry (image mirror steps are not covered)
Prerequisites:
- CLI
- kubectl
- eksctl
- helm
- aws (cli)
- aws-iam-authenticator (cli)
- General Access
- IBM entitled container registry (ibm-entitlement-key)
- IBM Fix Central (for APIC CRDs)
- Route53 public hosted zone with domain for creating wildcard subdomain A record
Create EKS Cluster
Using eksctl is the easiest way to spin up an EKS cluster. This command will create a cluster using node profile
c5.4xlarge of the following spec - CPU: 16, Memory: 32 Gib, Storage: EBS-Only, Network GBPs: Up to 10, EBS Mbs: 4,750.
Refer to eksctl doc for more information. https://eksctl.io/usage/creating-and-managing-clusters/
eksctl create cluster --name apic-eks --region us-east-1 --nodegroup-name apic-workers \--node-type c5.4xlarge --nodes 2 --ssh-access \--node-volume-size 120
Download APIC Related CRDs
Follow directions from the Knowledge Center and download the needed files.
For the purpose of this guide, some of the file samples are in this repo under directory sample-files. Other referenced files will be available in the apiconnect-operator-release-files_v10.0.1.0.zip (and within it the helper_files.zip) which can be downloaded from Fix Central.
Install Ingress and Cert Manager
# Install Nginx ingress controller - ingress-config.ymlhelm install ingress stable/nginx-ingress --values ./sample-files/ingress-config.yml --namespace kube-system# Create namespace for APICkubectl create ns apickubectl config set-context --current --namespace=apic# Install cert manager and ingress issuerskubectl apply -f cert-manager-0.10.1.yamlkubectl apply -f ingress-issuer-v1-alpha1.yaml -n apic# Check the certs are createdkubectl get certificates -n apic
NAME READY SECRET AGEanalytics-client-client True analytics-client-client 5m36sanalytics-ingestion-client True analytics-ingestion-client 5m36sgateway-client-client True gateway-client-client 5m36sgateway-peering True gateway-peering 5m36sgateway-service True gateway-service 5m36singress-ca True ingress-ca 5m36sportal-admin-client True portal-admin-client 5m36s
You should see the ELB and its external IP created by AWS when you run the following:
$ kubectl get svc -n kube-systemNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEingress-nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.100.113.63 afba042c90aa446c29917e5930bb1d73-2129028543.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31751/TCP,443:30345/TCP 4d7hingress-nginx-ingress-default-backend ClusterIP 10.100.167.4 <none> 80/TCP 4d7hkube-dns ClusterIP 10.100.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 4d8h
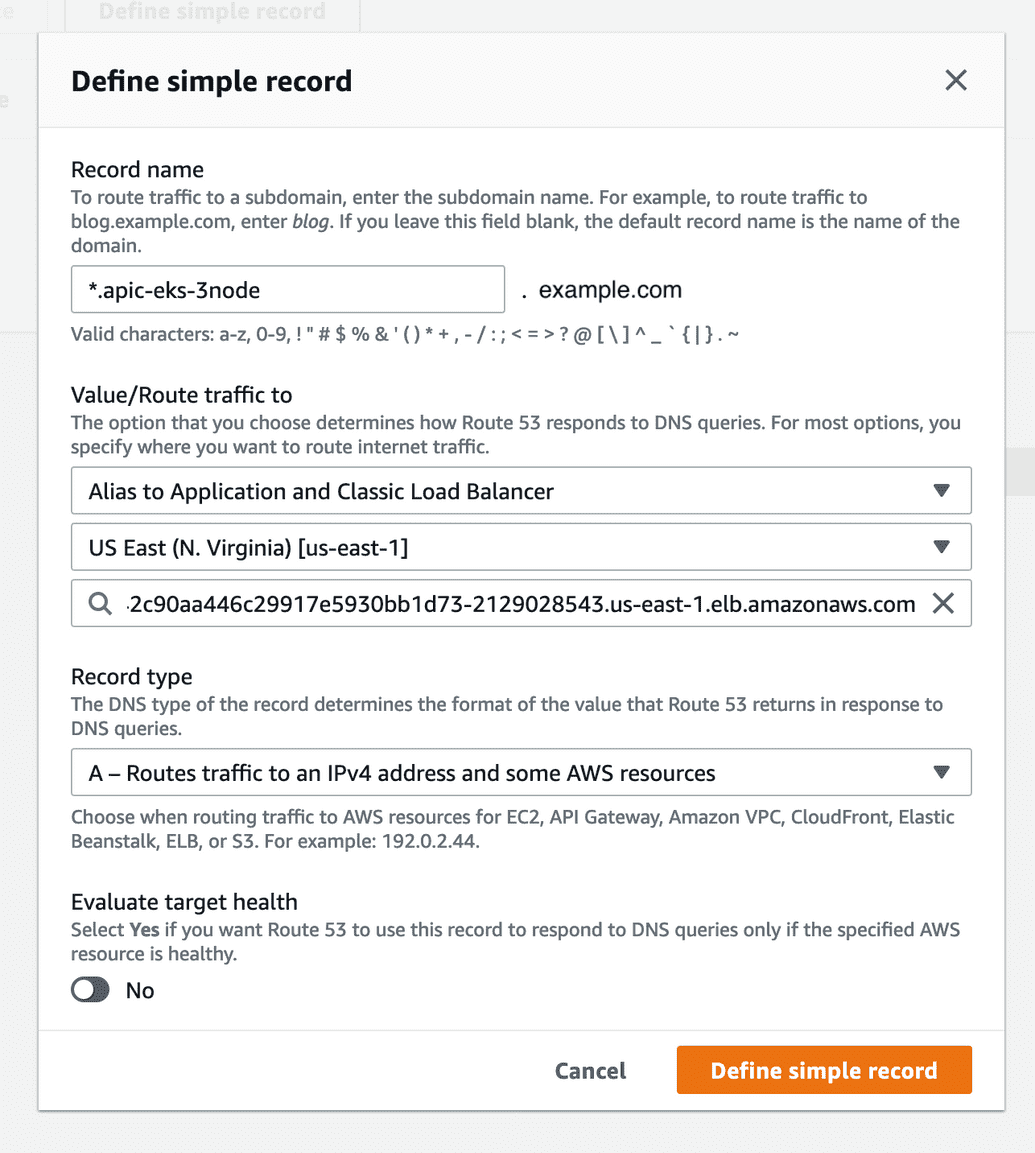
Configure Route53 DNS
Assuming the account has a Route53 public domain, we can create a wildcard subodmain record with name "*.apic-eks-3node" that points to the ELB created by the ingress controller above. This will be the subdomain hostname that we'll configured for the hosts field in the CR customization in the yaml files.
Apply CRDs and Customize APIC Subsystem Deployment
I've created custom CRs for the this guide. Please modify the values in each CR that's being applied as needed.
NOTE: for the four files *_cr.yaml under sample-files, replace $HOSTNAME with the wildcard domain that we created above (e.g. apic-eks-3node.example.com for this example)
Other files are available in the apiconnect-operator-release-files_v10.0.1.0.zip (and within it the helper_files.zip) which can be downloaded from Fix Central.
kubectl apply -f ibm-apiconnect-crds.yaml# In this guide I'll be using the entitled registry, so# we'll need a pull secret for the imageskubectl create secret docker-registry ibm-entitlement-key --docker-server=cp.icr.io \--docker-username=cp --docker-password=<ENTITLEMENT_KEY> -n apic# Install Operators in APIC namespace, pointing to entitled registry and uses IBM entitlement key by defaultkubectl apply -f ./sample-files/ibm-apiconnect.yamlkubectl apply -f ./sample-files/ibm-datapower.yaml# Edit CRs and apply themkubectl apply -f ./sample-files/management_cr.yamlkubectl apply -f ./sample-files/portal_cr.yaml# Gatewaykubectl apply -f ./sample-files/dp-admin-secret.yamlkubectl apply -f ./sample-files/apigateway_cr.yamlkubectl apply -f ./sample-files/analytics_cr.yaml
After the deployment is complete, you should see something like the following when running kubectl get pods
$ kubectl get podsNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEanalytics-cj-rollover-1603388700-hxlnt 0/1 Completed 0 15manalytics-client-cdfd8f94f-wjhmp 1/1 Running 0 4h11manalytics-ingestion-b4459548d-5xcp6 1/1 Running 0 4h11manalytics-mtls-gw-695856497d-4dntr 1/1 Running 0 4h10manalytics-storage-coord-9f75d69d6-jrz7j 1/1 Running 0 4h11manalytics-storage-data-0 1/1 Running 0 4h11manalytics-storage-master-0 1/1 Running 0 4h11mbackrest-backup-management-2a4f97b9-postgres-t2bt2 0/1 Completed 0 29hdatapower-operator-6856f485bb-fjntd 1/1 Running 0 3h20mdatapower-operator-conversion-webhook-78bdbcdc59-2gpqk 1/1 Running 0 3h20mgateway-0 1/1 Running 0 29hibm-apiconnect-6579f568f-kvth2 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-2a4f97b9-postgres-757f467dff-4lzxx 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-2a4f97b9-postgres-backrest-shared-repo-6ff9759dwgjvn 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-2a4f97b9-postgres-pgbouncer-7b6c7b7548-s6vc8 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-2a4f97b9-postgres-stanza-create-75r4d 0/1 Completed 0 29hmanagement-analytics-proxy-5cfc5d9c87-5vwql 1/1 Running 0 28hmanagement-apim-8676f6d79b-gg2nr 1/1 Running 0 28hmanagement-client-downloads-server-56464d597c-78sgz 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-juhu-cf497ff98-hbmrb 1/1 Running 0 28hmanagement-ldap-cf4fc7bc-mzp5c 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-lur-767c6b7b74-v9gjn 1/1 Running 0 28hmanagement-nats-operator-66b97844dd-gzhr6 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-nats-streaming-operator-5d77b5fc66-4frj5 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-natscluster-1 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-portal-proxy-78884ddfc-fstjj 1/1 Running 0 28hmanagement-stancluster-1 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-taskmanager-644dfd48b5-rmb8n 1/1 Running 0 28hmanagement-ui-698dd4f45c-gz7qt 1/1 Running 0 29hmanagement-up-apim-data-populate-0-to-6-8055ab6f-wlv7g 0/1 Completed 0 29hmanagement-up-apim-schema-0-to-6-8055ab6f-q9bm6 0/1 Completed 0 29hmanagement-up-lur-data-populate-0-to-2-8055ab6f-p4m8t 0/1 Completed 0 29hmanagement-up-lur-schema-0-to-2-8055ab6f-l895h 0/1 Completed 0 29hportal-5727ffec-db-0 2/2 Running 0 29hportal-5727ffec-www-0 2/2 Running 0 29hportal-nginx-675d6c6c69-g8xtm 1/1 Running 0 29hpostgres-operator-5b946c9c5-hk7lz 4/4 Running 0 29h
Then you should be able to see the ingress URLs from running kubectl get ingress
$ kubectl get ingressNAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGEanalytics-ac-endpoint ac.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 4h50manalytics-ai-endpoint ai.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 4h50mgateway-gateway rgw.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29hgateway-gateway-manager rgwd.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29hmanagement-admin admin.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29hmanagement-api-manager manager.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29hmanagement-consumer-api consumer.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29hmanagement-platform-api api.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29hportal-portal-director api.portal.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29hportal-portal-web portal.apic-eks-3node.example.com 1.2.3.4 80, 443 29h
Now we can navigate to the management-admin URL (e.g. admin.apic-eks-3node.example.com), and follow the Cloud Manager setup checklist.
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSMNED_v10/com.ibm.apic.cmc.doc/rapic_cmc_checklist.html
Update Node vm.max_map_count
For the analytics pods to come up successfully, we have to set vm.max_map_count on each node. Here's a handy command to do that, assuming ssh was enabled when the cluster is spun up, allowing the user to log in with the default SSH key/pair.
# 7th field is the external IP of the nodeskubectl get nodes -o wide --no-headers | awk '{print $7}' | xargs -I {} ssh-keyscan {} >> $HOME/.ssh/known_hostskubectl get nodes -o wide --no-headers | awk '{print $7}' | xargs -I {} ssh ec2-user@{} 'echo -e "\033[0;31m Setting {} \033[0m";sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144; echo "vm.max_map_count=262144" | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf'
Cluster Access/Management
Logging into a Cluster Node
Since we allowed SSH login from eksctl create cluster command, we
can login to the nodes and adjust node settings with ec2-user
# Get the public IPS for the nodekubectl get nodes -o widessh ec2-user@54.196.40.41
Cluster Access
$ aws configure --profile=clusterAdminAWS Access Key ID [None]: <access-key-id>AWS Secret Access Key [None]: <access-key>Default region name [None]: us-east-1Default output format [None]: json
export AWS_PROFILE=clusterAdmin
List Clusters
aws eks --region us-east-1 list-clusters
Update kubeconfig with a different cluster
aws eks --region us-east-1 update-kubeconfig --name apic-eks-3node
Deleting Cluster
Use the above commands to list out cluster names
eksctl delete cluster --name <cluster-name>
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/delete-cluster.html
References
Internal V10 EKS Install Guide https://github.ibm.com/apiconnect-field/apicv10EKS
AWS Instance Types https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/
IBM API Connect V10 Knowledge Center - Kubernetes Install https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSMNED_v10/com.ibm.apic.install.doc/capic_planning_deployment_kubernetes.html
Obtaining Install Files https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSMNED_v10/com.ibm.apic.install.doc/tapic_install_Kubernetes_firststeps.html
Initial Configuration Checklist https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSMNED_v10/com.ibm.apic.cmc.doc/rapic_cmc_checklist.html
Install eksctl https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/getting-started-eksctl.html#install-eksctl https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/create-cluster.html
Install kubectl https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/
Install Helm https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/
AWS CLI https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/install-cliv2.html
AWS IAM https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/install-aws-iam-authenticator.html