Shipping Container Management
Overview
Description: This microservice manages the container inventory. That is, this microservice will be in charge of keeping an inventory of all the containers registered in the system along with their status, size and location. When a new order is created and received, the container microservice will be in charge of assigning a container to this new shipping order based if a container is available that suits the order’s quantity and source port. Otherwise, will emit a ContainerNotFound event for the interested parties in the overall Reefer Container Shipment solution.
This microservice will also manage any container anomaly during the shipping of goods. That is, this microservice will monitoring ContainerAnomaly Events received for any particular container and in the case that these are received, it will mark the container for maintenance, send a OrderSpoilt Event so that any other microservice in the overall solution is aware that the fresh goods this container was carrying are now spoilt and will call a Business Process Manager (BPM) process in to automatically trigger the assignment of a field engineer to repair the container when it reaches the destination port.
This microservice is implemented with Spring Framework and runs on Tomcat.
Github repository: refarch-kc-container-ms
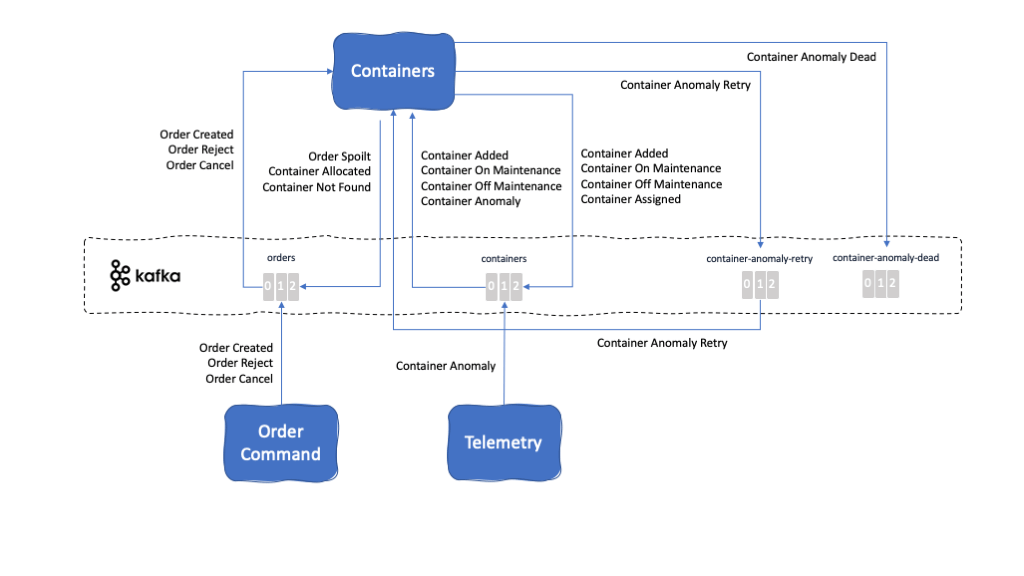
Kafka topics consumed from:
Kafka topics produced to:
Events reacted to:
- Order Created Event
- Order Reject Event
- Order Cancel Event
- Container Added Event
- Container Anomaly Event
- Container Anomaly Retry Event
- Container On Maintenance Event
- Container Off Maintenance Event
Events produced:
- Order Spoilt Event
- Container Allocated Event
- Container Not Found Event
- Container Assigned Event
- Container Anomaly Retry Event
- Container Anomaly Dead Event
- Container On Maintenance Event
- Container Off Maintenance Event
EDA Patterns implemented:
Build
This microservice is built using the Appsody development framework. The Appsody CLI is a required prerequisite for building the application locally.
Appsody will build the application by pulling the contents of the Appsody Stack it is based on and then performing the local application build inside the containerized environment:
appsody build -t <yournamespace>/kcontainer-spring-container-ms[:tag] [--push]
- You can optionally specify a container tag. If left blank,
latestwill be used. - You can optionally supply the
--pushflag to automatically push the built image to specified remote repository.
Performing an Appsody build will update the app-deploy.yaml file in the same directory with current information for the application image, labels, and annotations fields.
Run
Deployment parameters
The following deployment parameters are defined in the app-deploy.yaml file:
| Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| KAFKA_BROKERS | YES | Comma-separated list of Kafka brokers to connect to |
| KAFKA_APIKEY | NO | API Key used to connect to SASL-secured Kafka brokers. This is required when connecting to IBM Event Streams clusters. |
| TRUSTSTORE_ENABLED | NO | Required to be set to true when connecting to IBM Event Streams on the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I). |
| TRUSTSTORE_PATH | NO | The local path to the required truststore file when connecting to IBM Event Streams on CP4I. See Volume Mounts below. |
| TRUSTSTORE_PWD | NO | The password for the truststore file used for IBM Event Streams server verification. |
| KCSOLUTION_CONTAINERS_TOPIC | YES | The topic name used for communication relating to the containers entity. |
| KCSOLUTION_ORDERS_TOPIC | YES | The topic name used for communication relating to the orders entity. |
| KCSOLUTION_CONTAINER_ANOMALY_RETRY_TOPIC | YES | The topic name used for communication relating to the container anomaly retry actions. |
| KCSOLUTION_CONTAINER_ANOMALY_DEAD_TOPIC | YES | The topic name used for communication relating to the container anomaly dead letter actions. |
| POSTGRESQL_URL | YES | The URL of the PostgreSQL database instance in the form of jdbc:postgresql://<hostname>:<port>/<database-name>?sslmode=verify-full&sslfactory=org.postgresql.ssl.NonValidatingFactory. |
| POSTGRESQL_USER | YES | The username of the PostgreSQL database instance. |
| POSTGRESQL_PWD | YES | The password of the PostgreSQL database instance. |
| POSTGRESQL_CA_PEM | NO | Required when connecting to PostgreSQL instances that require SSL-based server verification, such as Databases for PostgreSQL on IBM Cloud. See Volume Mounts below. |
| ANOMALY_THRESHOLD | NO | The required number of container anomaly events a specific container must accrue before requiring maintenance. |
| BPM_ANOMALY | NO | Business process URL for the IBM BPM external system, which hosts the Container Anomaly business process. |
| BPM_ANOMALY_LOGIN | NO | Login URL for the IBM BPM external system, which hosts the Container Anomaly business process. |
| BPM_EXPIRATION | NO | Requested lifetime of the login token of the IBM BPM external system. |
| BPM_ANOMALY_USER | NO | Username for the IBM BPM external system, which hosts the Container Anomaly business process. |
| BPM_ANOMALY_PASSWORD | NO | Password for the IBM BPM external system, which hosts the Container Anomaly business process. |
Volume Mounts
The Container Management microservice requires up to two files to be injected at runtime for proper operation. As noted in the TRUSTSTORE_PATH and POSTGRESQL_CA_PEM parameters above, these files are SSL-based certificates which are required to verfiy the identity of the external service when calling it. These files are provided as --docker-options "-v host-src:container-dest ..." when running the microservice locally and as a Volume Mount when running the microservice on a Kubernetes cluster.
The TRUSTSTORE_PATH parameter is documented in the Event Streams Certificates section of the Prerequisites page. The Appsody run command should include a parameter similar to -v /Users/myuser/Downloads/es-cert.jks:/config/resources/security/es-ssl/es-cert.jks in its --docker-options string to run this microservice locally.
The POSTGRESQL_CA_PEM parameter is documented in the Creating Postgresql credentials as Kubernetes Secrets section of the Prerequisites page. The Appsody run command should include a parameter similar to -v /Users/myuser/Downloads/postgresql.crt:/.postgresql/postgresql.crt -v /Users/myuser/Downloads/postgresql.crt:/root/.postgresql/postgresql.crt in its --docker-options string to run this microservice locally.
Example: appsody run --docker-options "-v /Users/myuser/Downloads/es-cert.jks:/config/resources/security/es-ssl/es-cert.jks " ...
Running the microservice locally
When running the microservice locally, you must specify all the required deployment parameters from above as environment variables via the --docker-options flag being passed in from the Appsody CLI command.
Example: appsody run --docker-options "-e KAFKA_BROKERS=remotebroker1:9092,remotebroker2:9092 -e KCSOLUTION_CONTAINERS_TOPIC=containers -e KCSOLUTION_ORDERS_TOPIC=orders -v /Users/myuser/Downloads/es-cert.jks:/config/resources/security/es-ssl/es-cert.jks" ...
For more details on running the microservice locally, consult the Appsody run documentation as well as the deployment information contained in the app-deploy.yaml file.
Running the microservice remotely
The Appsody Operator is a required prerequisite for deploying the microservice to a remote Kubernetes or OpenShift cluster.
To deploy the microservice to a remote cluster:
appsody deploy <yournamespace>/kcontainer-spring-container-ms[:tag] --no-build
- You can omit the
--no-buildflag to have Appsody perform a build before deploying the application. - Note: Performing a build at deploy time requires specifying the absolute container reference path, as well as the
--pushflag. - The neccesary deployment parameter information will be read from the
app-deploy.yamlfile in the same directory.