Architecture Overview
Architecture
System Context
There are six main microservices implemented in this reference architecture. They each serve to fulfil the various parts of the Reefer Shipment Solution as outlined further below. When dealing with a microservices architecture, it is common to start with a high-level overview of the system and the entities that compose it, before drilling down into a more detailed view. The system context view for the solution can be seen in the diagram below:
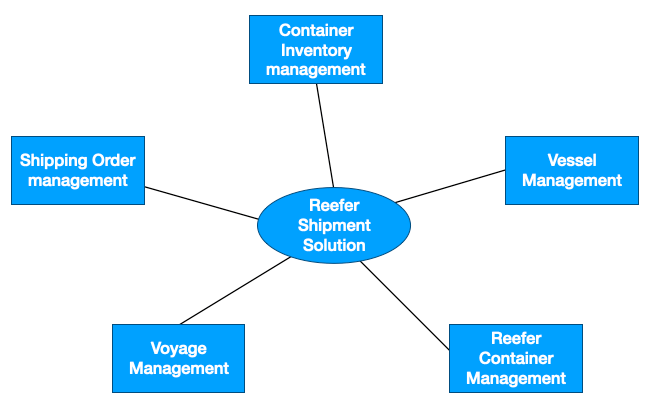
Components view
Deploying the different components using event-driven and microservice patterns, we organize them in the following figure (where the event backbone ensures pub/sub implementation and supports the event sourcing pattern):
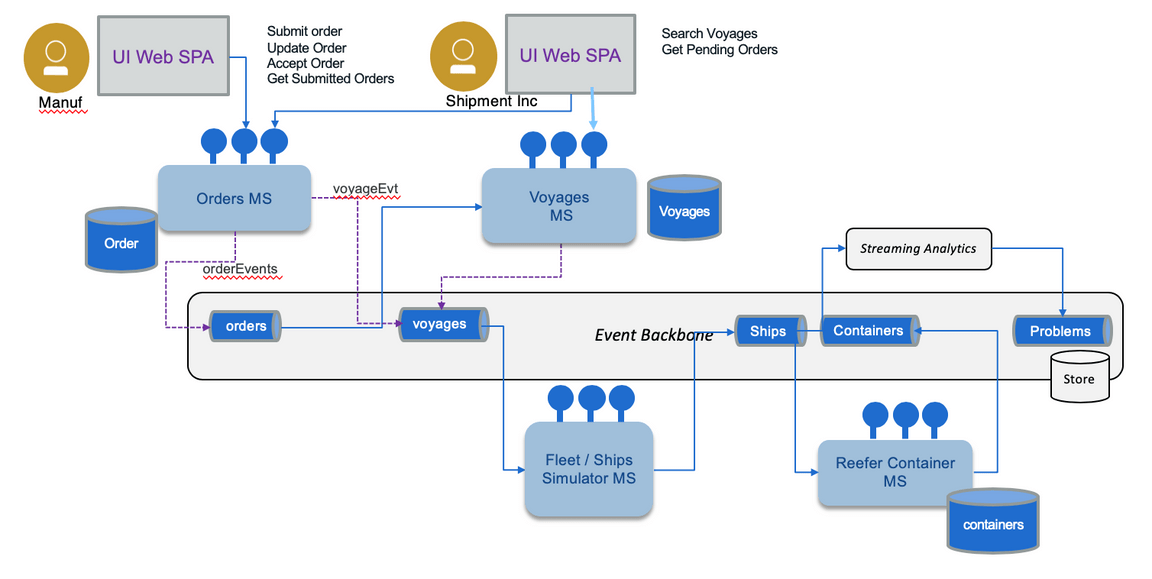
- Top left represents the user interface, implemented to support driving the Reefer Container Shipment solution. It includes a set of widgets to visualise the ships movements, the container tracking / monitoring and the event dashboards.
- The event backbone is used to define a set of topics used in the solution and as event sourcing for microservice to microservice data eventual consistency support.
- Each service supports the top-level process with a context boundary defining the microservice scope.
- Streaming analytics is used to process aggregates and analytics on containers and ship movement data ingested in real-time.
As we develop through multiple iterations, the current scope of the Minimum Viable Product is only addressing the following components:
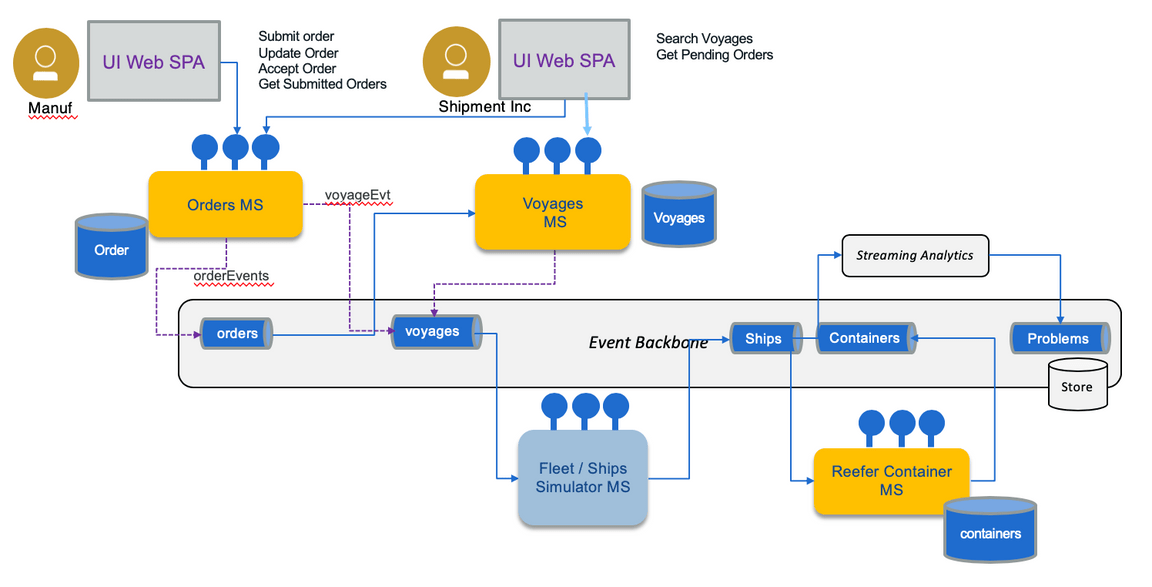
Which can also be represented in a deployment view as the figure below:
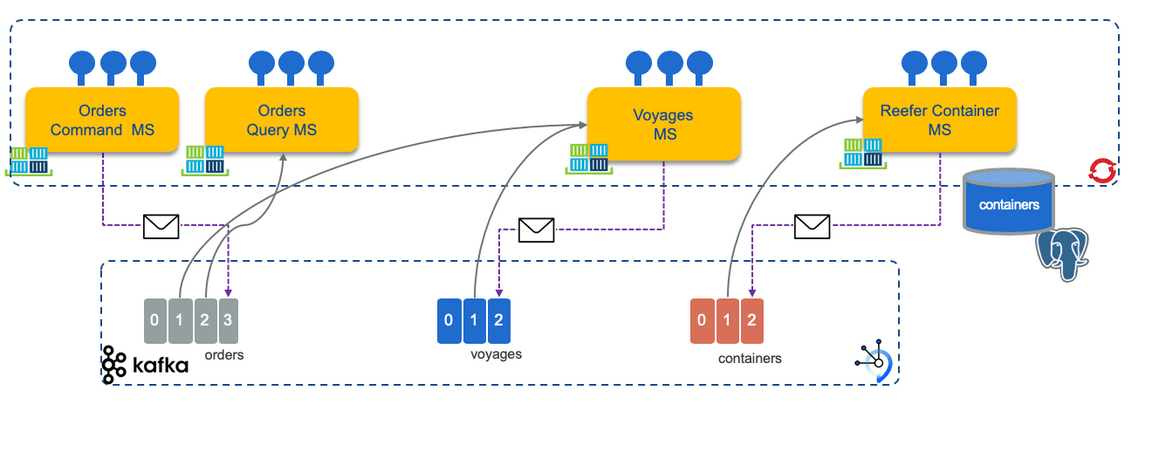
Summary of microservice scopes for shipment handling:
We are using a set of event-driven design patterns to develop the overall solution. One of them is the sub domain decomposition. From the analysis output, we have the aggregates, actors and data that are helping us to extract a set of subdomains.
NOTE: The details below are the initial outputs from the original event storming analysis and domain-driven design activities. However, the application model has evolved to keep up with the use case and the details for the currently implemented use case can be found on the Topics and Events pages.
- Fleet Service: responsible for managing the fleet of ships (container carriers), per major ocean.
- Information model:
- Fleet has multiple ships.
- Ship has unique identifier (we will use its name), a container capacity (represented as a matrix to make it simple), current position, status, voyage identifier for the voyage it is doing.
- Events: Ship commission, ship position, load container event, unload container event, start itinerary X, arrive at port, docked,…
- Operations: CRUD operations for Fleet and Ship management and the relationship between the two entities.
- Implementation: github.com/ibm-cloud-architecture/refarch-kc-ms
- Information model:
- Voyages Service: define a set of voyage schedules supported by the shipping company.
- Information model: voyageID, shipID, src_Port, planned_departure_date, dest_port, planned_arrival_dates, free_space_this_leg
- Events: add itinerary route, OrderAssigned
- Operations: CRUD on itinerary routes, query on capacity availability, assign slot to order, free slot for order.
- Implementation: github.com/ibm-cloud-architecture/refarch-kc-ms
- Order Service: manage the shipment order.
- Information model: Booking id , customer, pickup location, pickup after date, deliver location, expected deliver date, order status, assigned container
- Events: order placed, order assigned to voyage (sets VoyageID, ship ID), container assigned to order (sets container ID), Landorder, Transport associated with pickup container, Order status event, Order billing/accounting event
- Operations: CRUD on order, update order status
- Implementation: github.com/ibm-cloud-architecture/refarch-kc-order-ms
- Container Service:
- Information model: Container Id, Container temperature, container position, container condition ( maintenance goods), current associated order
- Events: order created, order assigned, container added, container anomaly, container maintenance, …
- Operations: CRUD on container
- Implementation: github.com/ibm-cloud-architecture/refarch-kc-container-ms