GitOps approach¶
What is covered¶
This GitOps supports bootstrapping the solution as a Day 1 operation, with the deployment of operators, secrets, pipelines... Then with Day 2 operations any changes to the configurations done in this repository, managed with the Git PR process, are propagated by ArgoCD to the runtime cluster.
The GitOps approach is an adaptation of Red Hat's KAM practices enhanced to be able to boostrap some important operators like the OpenShift GitOps Operator and OpenShift Pipelines Operator and Cloud Pak for integration operators.
kam bootstrap \
--service-repo-url https://github.com/ibm-cloud-architecture/refarch-eda-store-inventory \
--gitops-repo-url https://github.com/ibm-cloud-architecture/eda-rt-inventory-gitops \
--image-repo image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/ibmcase/ \
--output eda-rt-inventory-gitops \
--git-host-access-token <a-github-token> \
--prefix edademo --push-to-git=true
The generated content was enhanced to add boostraping configuration and scripts, the final repository structure includes:
- Boostrap folder: to install different operators and to define the ArgoCD project named
rt-inventory. - config folder, is for defining the ArgoCD apps and the app of apps.
- kconnect folder is used to build a custom docker image of Kafka connector with MQ source, Elasticsearch sink and Cloud Object storage sink.
- local-demo folder is for running the solution on your laptop using docker-compose.
- environments folder, is the most important one, it uses Kustomize to declare environments (dev, staging) and component deployments (See next section for details).
We also added a Makefile and scripts to deploy the gitops, pipelines operators and different elements with or without GitOps.
In this Gitops you can use different approaches to deploy the real-time inventory solution depending of your existing environment.
- Start from an OpenShift Cluster without any Cloud Pak for Integration components, this will take few hours to deploy as some Operator and Operand deployments may take time.
- Start from a Cloud Pak for integration deployed in cp4i-* projects
GitOps on new OpenShift Cluster¶
This GitOps repository (represented as the yellow rectangle in figure below) defines the ArgoCD apps used to monitor and deploy the different microservices, streaming processing apps, and the different IBM products needed: Event Streams, MQ, API management, event-end-point management. The figure belows presents the adopted strategy:
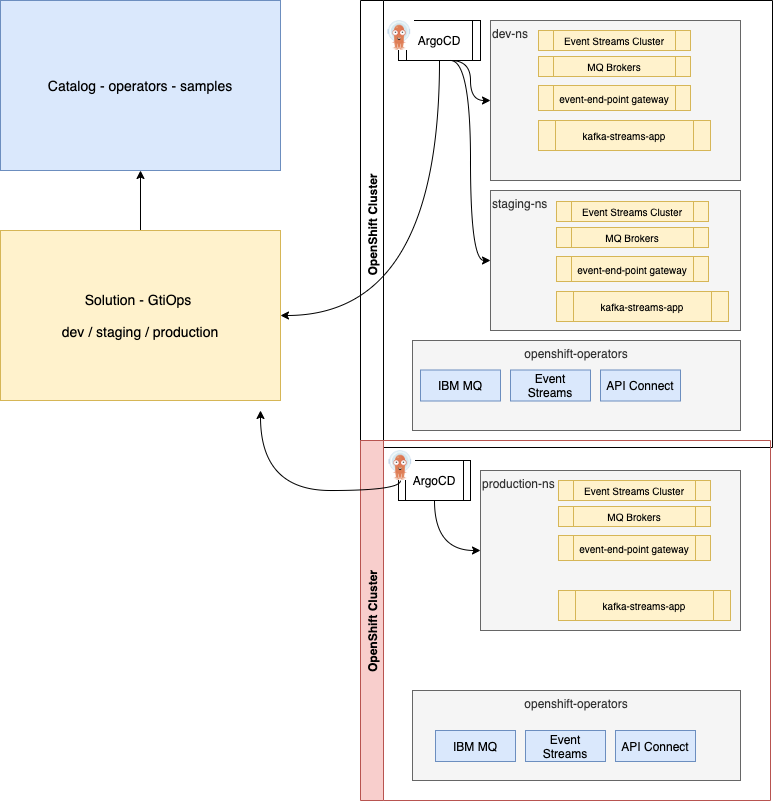
The gitops catalog repository, represented with a blue rectangle, defines the different operator subscriptions for the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration components. Centralizing to one repository such operator subscriptions enforces reuse between solutions.
What is deployed in this demonstration¶
The development project includes event-streams, MQ, schema registry...
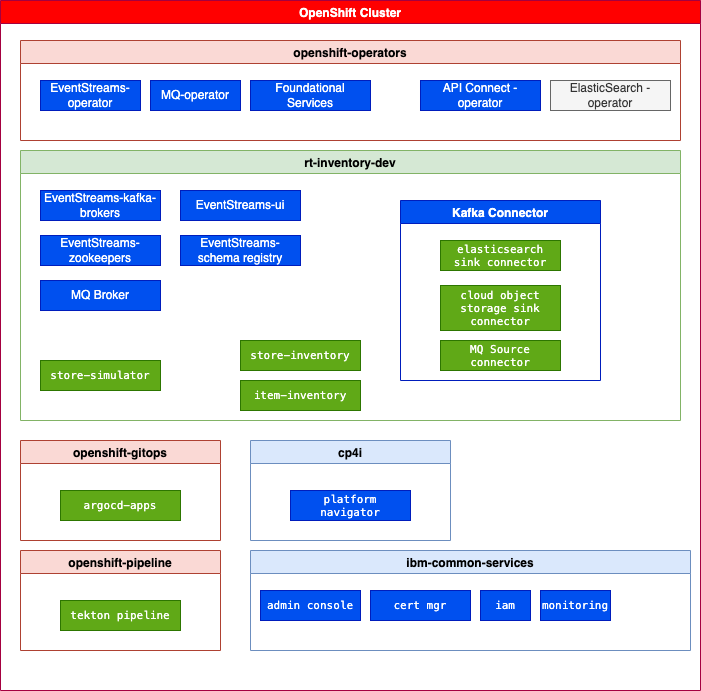
The installation approach is to deploy operators to manage All Namespaces, at the cluster scope. So only one Platform UI can be installed per cluster. A single instance of IBM Cloud Pak foundational services is installed in the ibm-common-services namespace.
The following operators may be installed from this GitOps:
- ibm-integration-platform-navigator
- ibm-integration-asset-repository
- ibm-integration-operations-dashboard
- ibm-eventstreams
- ibm-mq
The entitlement key secret will be copied to each namespace where some of the Cloud Pak integration products are deployed, using a kubernetes job.
Part of this deployment will be based on commands run from your laptop, part as pipelines, and part as ArgoCD apps. The approach is based on the following:
- secrets, and operators deployments to bootstrap the CI/CD are configured with Makefile and commands. Operators are deployed in
openshift-operators. - Tekton pipelines are used to deploy some CP4I operators
- ArgoCD apps are used to deploy CP4I operands: the use of ArgoCD for this, is justified for Day 2 operations.
The pipelines are using a service account, named pipeline, in the rt-inventory-cicd project, and cluster role to access different resources cross namespaces.
CP4Integration installation considerations¶
- In this solution, CP4I operators are deployed in All namespaces, the entire OpenShift cluster effectively behaves as one large tenant.
- With All namespace there can be only one Platform Navigator installed per cluster, and all Cloud Pak instances are owned by that Platform Navigator.
- A single instance of IBM Cloud Pak foundational services is installed in the
ibm-common-servicesnamespace if the foundational services operator is not already installed on the cluster. - Operators can be upgraded automatically when new compatible versions are available. For production deployment, the manual upgrade may be desirable.
Bootstrap GitOps¶
The current GitOps was run on OpenShift 4.8.
- Login to the OpenShift Console, and get login token to be able to use
oc cli -
Obtain your IBM license entitlement key and export as KEY environment variables
-
create
github-credentials.yamlfile for the git secret based ontemplate-github-credentials.yaml. Use your github personal access token. It will be used by the pipeline runs. - create a Secret for your IBM Cloud Object Storage credential. Use the on
template-cos-credentials.yamland modify the following parameters:
cos.api.key: <cos-credential.field.apikey>
cos.bucket.location: <region where the cos bucket is>
cos.bucket.name: <bucketname>
cos.service.crn: <cos-credential.field.iam_serviceid_crn>
- If not done already, use the following command to install GitOps and Pipeline operators, entitlement key, and IBM image catalog:
Once the operators are running the command: oc get pods -n openshift-gitops should return a list of pods like:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
openshift-gitops-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 4h5m
openshift-gitops-applicationset-controller-6948bcf87c-jdv2x 1/1 Running 0 4h5m
openshift-gitops-dex-server-64cbd8d7bd-76czz 1/1 Running 0 4h5m
openshift-gitops-redis-7867d74fb4-dssr2 1/1 Running 0 4h5m
openshift-gitops-repo-server-6dc777c845-gdjhr 1/1 Running 0 4h5m
openshift-gitops-server-7957cc47d9-cmxvw 1/1 Running 0 4h5m
- Deploy different IBM product Operators (Event Streams, MQ...) to monitor
All Namespaces:
The IBM common services deployment can take more than 30 minutes.
- Get the ArgoCD User Interface URL and open a web browser:
chrome https://$(oc get route openshift-gitops-server -o jsonpath='{.status.ingress[].host}' -n openshift-gitops)
Deploy ArgoCD app of apps:¶
- To start the Continuous Deployment with ArgoCD, just executing the following command should deploy event streams cluster instance, MQ broker, kafka connect, and the different microservices.
The expected set of ArgoCD apps looks like:

- rt-inventory-Argo-app is an app of apps
- rt-inventory-dev-env is for the rt-inventory-dev namespace
- rt-inventory-dev-services is for event streams, kafka connect cluster and mq deployments in dev-env namespace
- rt-inventory-store-simulator-app is for the simulator app used in the demo.
- rt-inventory-item-inventory for the item aggregator application
- rt-inventory-store-inventory for the store aggregator application
Potential errors¶
-
"ConfigMap ibm-common-services-status in kube-public to be ready"
- While the Event Streams cluster is created: An unexpected exception was encountered: Exceeded timeout of 1200000ms while waiting for ConfigMap resource ibm-common-services-status in namespace kube-public to be ready. More detail can be found in the Event Streams Operator log.
- This is an issue known as of 10.5. Restart the ES operator pod
- See also https://github.ibm.com/mhub/qp-planning/issues/7383
Configure connector¶
- Go to the dev project:
oc project rt-inventory-dev -
Deploy the sink kafka connector for cloud object storage:
-
Modify the file
kafka-cos-sink-connector.yamlinenvironments/rt-inventory-dev/apps/cos-sink, by replacing the following line from the cloud object storage credentials:
cos.api.key: IBM_COS_API_KEY
cos.bucket.location: IBM_COS_BUCKET_LOCATION
cos.bucket.name: IBM_COS_BUCKET_NAME
cos.bucket.resiliency: IBM_COS_RESILIENCY
cos.service.crn: "IBM_COS_CRM"
-
Then deploy the connector:
oc apply -f environments/rt-inventory-dev/apps/cos-sink/kafka-cos-sink-connector.yaml -
Deploy the MQ source connector
- Access to the Simulator User Interface via:
- Access Event Stream Console:
- Access to IBM MQ Admin Console
Deploy in an existing CP4I deployment¶
In this section we suppose CP4I is already deployed in cp4i namespace, event streams in cp4i-eventstreams project. So somewhere someone has already deployed the infrastructure, and other components as multi tenants. (This is represented as the green rectangles in the figure below)

Some particularities:
- Event Streams is in its own project, so kafka topics, kafka users has to follow a naming convention to avoid colision with other teams / solutions.
- MQ broker runs local to the solution namespace. (
rt-inventory-devhas its own MQ Broker)
The command below will not use GitOpa / ArgoCD
- Get Store Simulator URL and execute the demonstration script:
Bootstrap GitOps¶
- Login to the OpenShift Console, and get login token to be able to use
oc cli - If not done already, use the script to install GitOps and Pipeline operators:
- Create an ArgoCD project named
rt-inventory
-
To get the
adminuser's password use the command -
Get the ArgoCD User Interface URL and open a web browser
chrome https://$(oc get route openshift-gitops-server -o jsonpath='{.status.ingress[].host}' -n openshift-gitops)
Deploy the solution¶
- To start the Continuous Deployment with ArgoCD, just executing the following command should deploy different microservices under rt-inventory-dev project using event-streams, MQ.. from another project (e.g. cp4i).